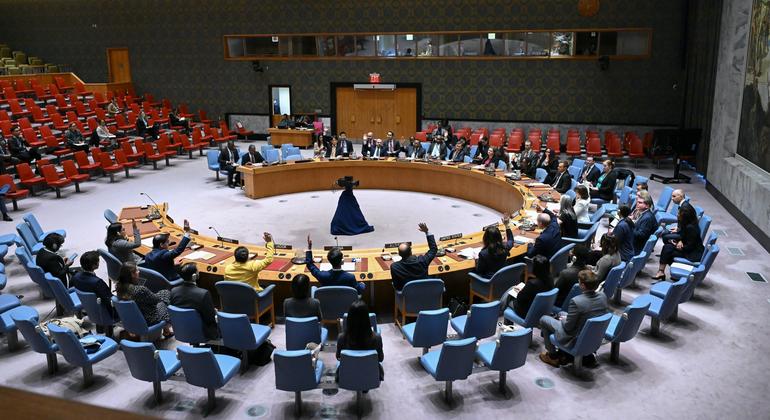
The United Nations Security Council unanimously adopted resolution 2752 (2024) under Chapter VII of the UN Charter, declaring that the situation in Haiti poses a threat to international peace and security in the region. This resolution extends sanctions measures previously imposed in order to prevent the supply of weapons and military equipment to criminal gangs operating in Haiti.
The island nation of Haiti is currently facing a multifaceted humanitarian crisis, exacerbated by widespread violence perpetrated by armed criminal groups. This crisis is unfolding against a backdrop of natural disasters and economic instability, further complicating efforts to address the situation. Hundreds of thousands of people have been forced to flee their homes, including approximately 350,000 children. Reports of sexual violence, kidnappings, and executions further underscore the gravity of the situation.
One of the key provisions of the resolution is the provision of exemptions for supplies that support UN or UN-authorised missions as well as for Haitian security forces. Non-lethal military equipment intended for humanitarian or protective purposes, along with related technical assistance or training, is also exempt from the sanctions. This exemption is crucial for supporting efforts to promote peace and stability in Haiti.
In 2023, the Security Council authorized the deployment of a Multinational Security Support (MSS) mission to Haiti, aimed at assisting the national police in addressing the escalating gang violence. This mission, led by Kenya, currently consists of around 410 police officers on the ground, with plans to expand to approximately 2,500 personnel. Despite these efforts, Haiti continues to grapple with a deepening crisis, underscoring the urgent need for collective action.
The resolution also emphasizes the importance of preventing illicit arms trafficking and calls for enhanced coordination among the UN, regional organizations, and the Haitian government to strengthen border security and manage weapons stockpiles effectively. It specifically urges the Haitian government to bolster the capacity of its national police force in controlling weapons and ammunition, including through strengthening border and customs controls.
Furthermore, the resolution renews the mandate of the sanctions committee and extends the work of the Panel of Experts for an additional 13 months. The committee is responsible for updating the list of individuals and entities subject to sanctions, particularly those involved in violating the arms embargo. The resolution also sets forth benchmarks for lifting sanctions, including reductions in armed violence, improvements in the rule of law, and decreased arms trafficking. The Secretary-General of the UN is tasked with assessing progress in meeting these benchmarks by October 2025.
Overall, the adoption of resolution 2752 (2024) underscores the international community’s commitment to addressing the crisis in Haiti and promoting peace and stability in the region. By extending sanctions measures and providing exemptions for critical supplies, the Security Council aims to support efforts to mitigate the humanitarian crisis and combat the escalating violence in the country. However, the challenges facing Haiti remain significant, underscoring the need for sustained and coordinated action to address the root causes of the crisis and pave the way for a sustainable and peaceful future for the people of Haiti.